Preparing for an IPO (CFI)
By CFI, Corporate Finance Institute.
Source blog post: https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/knowledge/finance/ipo-process/
What is the IPO Process?
The Initial Public Offering IPO Process is where a previously unlisted company sells new or existing securities and offers them to the public for the first time.
Prior to an IPO, a company is considered to be private – with a smaller number of shareholders, limited to accredited investors (like angel investors/venture capitalists and high net worth individuals) and/or early investors (for instance, the founder, family, and friends).
After an IPO, the issuing company becomes a publicly listed company on a recognized stock exchange. Thus, an IPO is also commonly known as “going public”.

Overview of the IPO Process
This guide will break down the steps involved in the process, which can take anywhere from six months to over a year to complete.
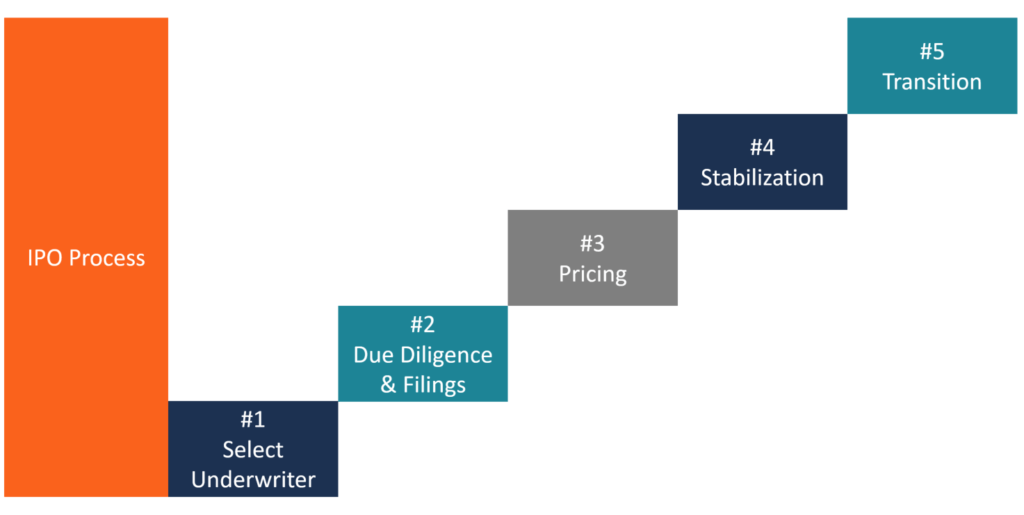
Below are the steps a company must undertake to go public via an IPO process:
Select a bank
Due diligence and filings
Pricing
Stabilization
Transition

Step 1: Select an investment bank
The first step in the IPO process is for the issuing company to choose an investment bank to advise the company on its IPO and to provide underwriting services. The investment bank is selected according to the following criteria:
Reputation
The quality of research
Industry expertise
Distribution, i.e., if the investment bank can provide the issued securities to more institutional investors or to more individual investors
Prior relationship with the investment bank
Step 2: Due diligence and regulatory filings
Underwriting is the process through which an investment bank (the underwriter) acts as a broker between the issuing company and the investing public to help the issuing company sell its initial set of shares. The following underwriting arrangements are available to the issuing company:
Firm Commitment: Under such an agreement, the underwriter purchases the whole offer and resells the shares to the investing public. The firm commitment underwriting arrangement guarantees the issuing company that a particular sum of money will be raised.
Best Efforts Agreement: Under such an agreement, the underwriter does not guarantee the amount that they will raise for the issuing company. It only sells the securities on behalf of the company.
All or None Agreement: Unless all of the offered shares can be sold, the offering is canceled.
Syndicate of Underwriters: Public offerings can be managed by one underwriter (sole managed) or by multiple managers. When there are multiple managers, one investment bank is selected as the lead or book-running manager. Under such an agreement, the lead investment bank forms a syndicate of underwriters by forming strategic alliances with other banks, each of which then sells a part of the IPO. Such an agreement arises when the lead investment bank wants to diversify the risk of an IPO among multiple banks.
An underwriter must draft the following documents:
Engagement Letter: A letter of engagement typically includes:
Reimbursement clause: This clause mandates that the issuing company must cover all out-of-the-pocket expenses incurred by the underwriter, even if the IPO is withdrawn during the due diligence stage, the registration stage, or the marketing stage.
Gross spread/underwriting discount: Gross spread is arrived at by subtracting the price at which the underwriter purchases the issue from the price at which they sell the issue.
Gross spread = Sale price of the issue sold by the underwriter – Purchase price of the issue bought by the underwriter
Typically, the gross spread is fixed at 7% of the proceeds. The gross spread is used to pay a fee to the underwriter. If there is a syndicate of underwriters, the lead underwriter is paid 20% of the gross spread. 60% of the remaining spread, called “selling concession”, is split between the syndicate underwriters in proportion to the number of issues sold by the underwriter. The remaining 20% of the gross spread is used for covering underwriting expenses (for instance, roadshow expenses, underwriting counsel, etc.).
Letter of Intent: A letter of intent typically contains the following information:
The underwriter’s commitment to enter an underwriting agreement with the issuing company
A commitment by the issuing company to provide the underwriter with all relevant information and, thus, fully co-operate in all due diligence efforts.
An agreement by the issuing company to provide the underwriter with a 15% overallotment option.
The letter of intent does not mention the final offering price.
Underwriting Agreement: The letter of intent remains in effect until the pricing of the securities, after which the Underwriting Agreement is executed. Thereafter, the underwriter is contractually bound to purchase the issue from the company at a specific price.
Registration Statement: The registration statement consists of information regarding the IPO, the financial statements of the company, the background of the management, insider holdings, any legal problems faced by the company, and the ticker symbol to be used by the issuing company once listed on the stock exchange. The SEC requires that the issuing company and its underwriters file a registration statement after the details of the issue have been agreed upon. The registration statement has two parts:
The Prospectus: This is provided to every investor who buys the issued security
Private Filings: this is comprised of information which is provided to the SEC for inspection but is not necessarily made available to the public
The registration statement ensures that investors have adequate and reliable information about the securities. The SEC then carries out due diligence to ensure that all the required details have been disclosed correctly.
Red Herring Document: In the cooling-off period, the underwriter creates an initial prospectus which consists of the details of the issuing company, save the effective date and offer price. Once the red herring document has been created, the issuing company and the underwriters market the shares to public investors. Often, underwriters go on roadshows (called the dog and pony shows – lasting for 3 to 4 weeks) to market the shares to institutional investors and evaluate the demand for the shares.
Step 3: Pricing
After the IPO is approved by the SEC, the effective date is decided. On the day before the effective date, the issuing company and the underwriter decide the offer price (i.e., the price at which the shares will be sold by the issuing company) and the precise number of shares to be sold. Deciding the offer price is important because it is the price at which the issuing company raises capital for itself. The following factors affect the offering price:
The success/failure of the roadshows (as recorded in the order books)
The company’s goal
Condition of the market economy
IPOs are often underpriced to ensure that the issue is fully subscribed/ oversubscribed by the public investors, even if it results in the issuing company not receiving the full value of its shares.
If an IPO is underpriced, the investors of the IPO expect a rise in the price of the shares on the offer day. It increases the demand for the issue. Furthermore, underpricing compensates investors for the risk that they take by investing in the IPO. An offer that is oversubscribed two to three times is considered to be a “good IPO.”
Step 4: Stabilization
After the issue has been brought to the market, the underwriter has to provide analyst recommendations, after-market stabilization, and create a market for the stock issued.
The underwriter carries out after-market stabilization in the event of order imbalances by purchasing shares at the offering price or below it.
Stabilization activities can only be carried out for a short period of time – however, during this period of time, the underwriter has the freedom to trade and influence the price of the issue as prohibitions against price manipulation are suspended.
Step 5: Transition to Market Competition
The final stage of the IPO process, the transition to market competition, starts 25 days after the initial public offering, once the “quiet period” mandated by the SEC ends.
During this period, investors transition from relying on the mandated disclosures and prospectus to relying on the market forces for information regarding their shares. After the 25-day period lapses, underwriters can provide estimates regarding the earning and valuation of the issuing company. Thus, the underwriter assumes the roles of advisor and evaluator once the issue has been made.
Metrics for judging a successful IPO process
The following metrics are used for judging the performance of an IPO:
Market Capitalization: The IPO is considered to be successful if the company’s market capitalization is equal to or greater than the market capitalization of industry competitors within 30 days of the initial public offering. Otherwise, the performance of the IPO is in question.
Market Capitalization = Stock Price x Total Number of Company’s Outstanding Shares
Market Pricing: The IPO is considered to be successful if the difference between the offering price and the market capitalization of the issuing company 30 days after the IPO is less than 20%. Otherwise, the performance of the IPO is in question.